Graphing and Animating parameters
Expressing symbolic conditions at interval's bounds
Three functions f, g and h are considered:
f is defined on (–∞ ; – 1] by f(x) = – 1 ;
g is defined on [ 1 ; + ∞) by g(x) =1 ;
h is defined on [ -2 ; 1] by h(x) = a x3 + b x ;
The goal is to find values of a and b connecting “smoothly” the three graphs and to create a piecewise defined function.
Create the functions f, g, h (as in first example), entering the correct domains of definition. You will be prompted to accept the creation of parameters a and b.
Graphing and Animating parameters
Press the buttons f, g, and h in the graphic tab. The graph of h is updated according to values of a and b
Initially a cursor is visible. You can make it (des)appear by clicking on the identifyer
![]()

Figure 50 - cursors visible Figure 51 - cursor invisible
When the cursor is visible, you can animate the parameter with the mouse or the keyboard's arrows.
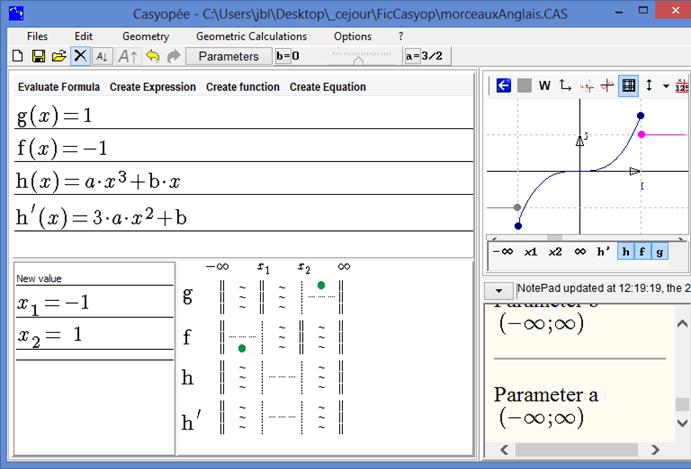
Figure 52 - Displaying functions f, g and h
By animating parameters, one can try to approach a solution. For instance with a=-1 and b= 2, the graphs are connected, but the connexion is not smooth. That is why we need to solve the problem symbolically.
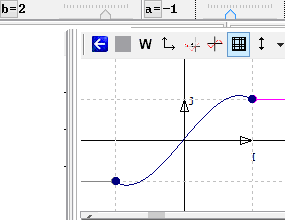
Figure 53 - Graphs connected by parameter animation
Expressing symbolic conditions at interval's bounds
Verify that parameters are not instantiated (see Figure 50 - Instantiated parameters in toolbar Figure 51 - Formal parameter).
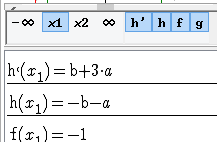
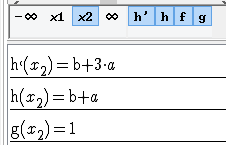
Press the button with x0 then x1 in the command bar at the bottom of the graphic tab.
The symbolical value list helps to express algebraically the conditions.
|
Figure 54 - Value for x1 with parameters a and b |
Figure 55 - Values for x2 with parameters a and b |
Then the conditions are b +a = 1 (value in 1 and -1) and 3a + b = 0 (null derivative in 1 and -1);
By solving this system, you can obtain suitable values for a and b (a = -1/2 and b =3/2).
Note: Casyopée does not solve systems. Here a solution could be obtained by successively solving one equation in a, then substituting in the second equation and solving in b. Experts can use Evaluate Formula in the Algebra tab menu, and choose Maxima in Syntax for Entry.
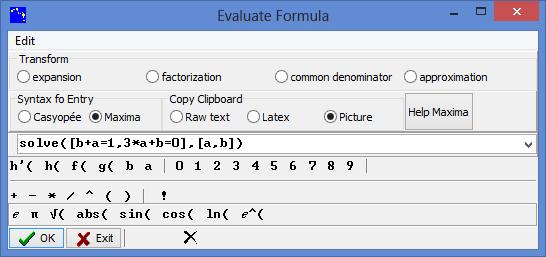
Figure 56 - Solving a system with Maxima
You obtain a solution in the NotePad: ![]() . Alternatively, you could have entered a formula like solve([h(1)=1 , h’(1)=0],[a,b]).
. Alternatively, you could have entered a formula like solve([h(1)=1 , h’(1)=0],[a,b]).
Instanciating parameters in expressions
When calculating and resolving equations, Casyopée considers any parameter to be a symbolic value. This is why, by default, the parameters are not "instantiated" in the algebraic pane displays (list of expressions, values of the variable,) and in the table of symbolic values. It is possible to instantiate one or more parameters in an expression thanks to the contextual menu (right click). When you check the parameter (s), the expression is displayed in a special way.
The values or limits of a function displayed in the list of symbolic values are instantiated according to the choices made for the expression defining this function.
Substituting parameters
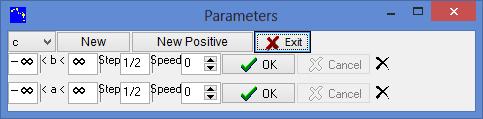
Animate the parameters to give them the values of the solution and check on the graph. You may have to adapt the step, that is to say the increment for each move of the cursor; use the Parameters button, then in the Step box put 1/2 for the increment.
Select the function h, click on Calculate, choose substitute; parameters a and b values are taken into account.

Figure 57 - Menu Calculate / substitute
Figure 58 - Confirmation box for substitution
A new function h0, independent of the function h, has been created.
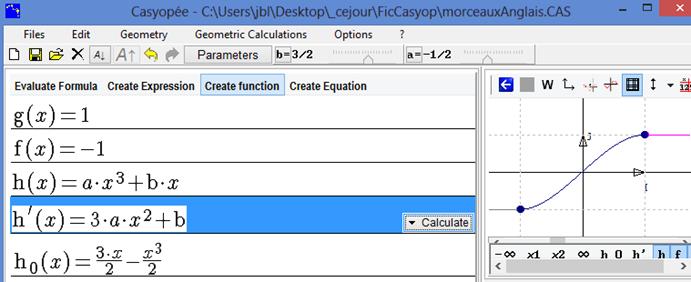
Figure 59 - Graphic displaying of substitution

 Preview
Preview
 Print...
Print...


