First case: the locus is included inside a geometrical object (straight line or circle)
Second case: the locus is the curve of a real-valued function
General case: the locus is a parametric curve
First case: the locus is included inside a geometrical object (straight line or circle)
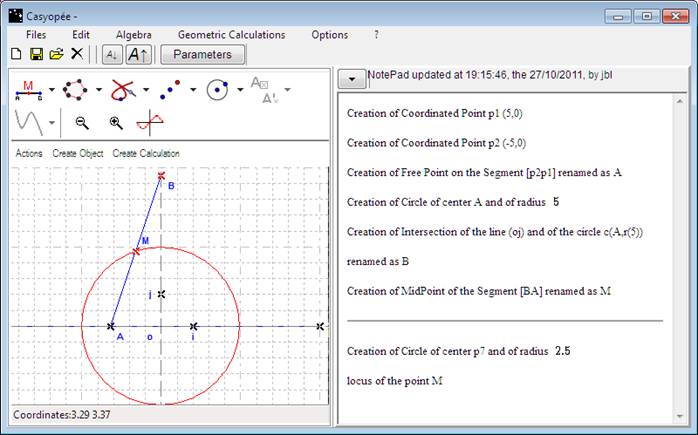
Consider the following problem: [AB] is a segment of fixed length 5, A being on the x-axis and B on the « positive » half-line of the y-axis. We are looking for the locus of M midpoint of [AB]
Figure 135 gives the steps of the construction. Like in Geogebra, the locus entry is in the menu for lines![]() . Select the point with the mouse and then a free point or a parameter (cursor) on which the point is dependinge. Here, Casyopée recognizes that the locus is included in the circle centred in o and of radius 2.5. Actually M describes only the upper half circle.
. Select the point with the mouse and then a free point or a parameter (cursor) on which the point is dependinge. Here, Casyopée recognizes that the locus is included in the circle centred in o and of radius 2.5. Actually M describes only the upper half circle.
Figure 135- Locus of the midpoint of a segment of fixed length, whose vertexes are on the axes
Second case: the locus is the curve of a real-valued function
We are now looking for the locus of N midpoint of [MB]
Casyopée creates a real-valued function and then the corresponding curve, as indicated in the NotePad. We recognize a half ellipse (Figure 136).
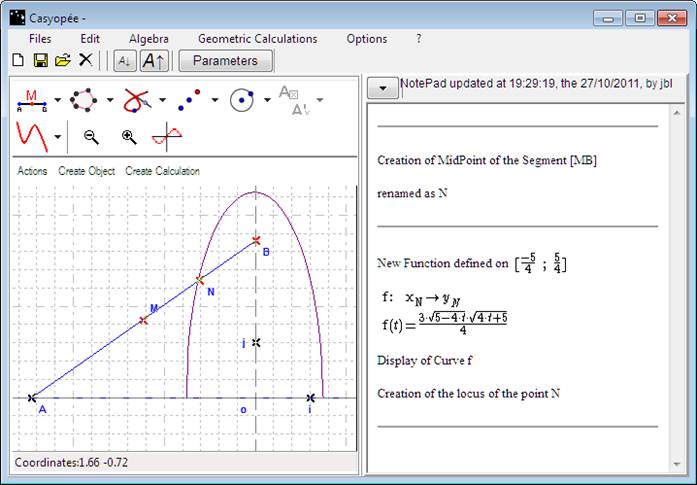
Figure 136- Locus of a fixed point on a segment of fixed length, whose vertexes are on the axes
General case: the locus is a parametric curve
Construction of a parabola by directrix and focus
If the directrix is horizontal, like in the second case above, the locus will be the curve of a real valued function. Then we take here (ij) as a directrix and o as a focus. The NotePad shows that Casyopée created the locus by computing a new geometrical function with values in IR² and displaying the corresponding parametric curve. Note that Casyopée chose the identifier t in order to avoid confusion.
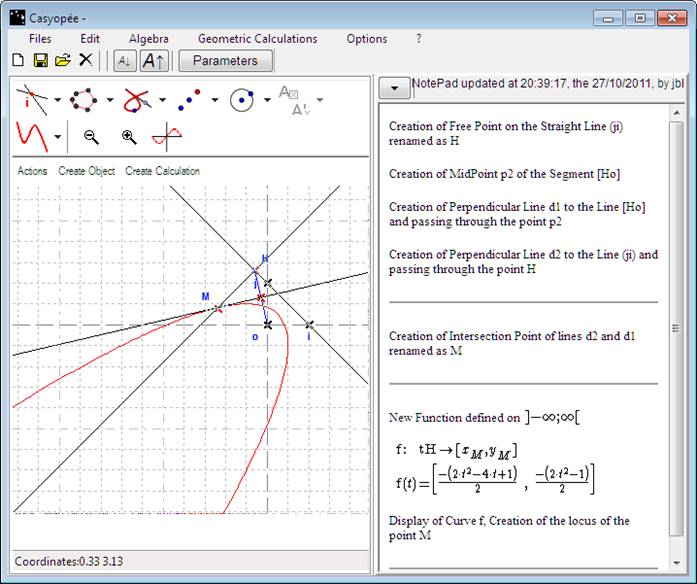
There is a two way link between the free point (here A) and the pointer on the graphs of the function with values in IR².


 Preview
Preview
 Print...
Print...


